GOOGLE TAG MANAGER FOR BEGINNERS

Whether you’re an SEO specialist or digital marketing manager, you know that online campaigns are measured by one thing: results. But without sufficient data, you’re essentially running them blind. Google Analytics illuminates some key insights. Still, it alone can leave businesses with blind spots. Tagging in some help from Google Tag Manager (GTM) broadens your view, giving you a fuller picture of how users are interacting with your site.
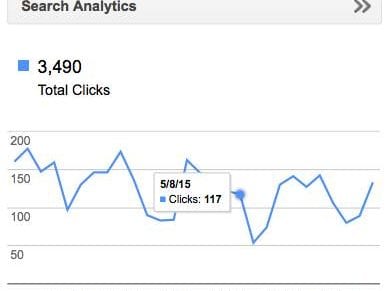
Want to know how a visitor arrived on your site or what outbound clicks they made while browsing? GTM will track any and all activity you outline. The best part is that you don’t have to be a programmer or web developer to implement tags or make important tracking modifications to your site. It leaves your source code intact, freeing the dev team to focus on more complex projects.
For a small snippet of code, there’s a lot of available info. This post covers the basics so marketers can feel confident enough to start working with Google Tag Manager.
Tracking with GTM
Tags collect site information across numerous verticals. Have an activity you want to isolate? Once the container code is added to your pages, you simply use Google Tag Manager’s user-friendly interface to add or make edits from the web.
Use it to track tangible results about your digital marketing campaigns on key metrics like:
- scroll tracking
- form submissions
- conversions
- heat mapping
- remarketing
- file downloads
It’s worth noting that GTM is also universal. Though the Google product works seamlessly with services like Adwords, it also plays well with third party tags from sites like Twitter or Crazy Egg.
Setting up Google Tag Manager
Ready to make tracking codes work for you? Follow these steps to better measure the results of your digital marketing efforts:
- Log in to the Google Tag Manager page – tagmanager.google.com. (First, make sure you’re signed in to your Google Analytics account if you have one.)
- Set up your account name (usually your company name).
- Pick and name your container (web vs mobile vs AMP, etc).
- Check the service agreement and “create.”
At this point, you may need a developer to help you implement two pieces of script to every page of your site. It’s a good idea to have them help remove any existing tags from your site’s source code and add any customized tags outside the GTM tag templates while they’re at it.
Next, spend a little time learning about triggers and variables in GTM’s help section. It also covers more advanced features like Data Layers and debugging options.
Help with GTM
In the beginning, you’re likely to have questions or issues within GTM. Fortunately, many of the most common conundrums are covered in popular Google forums. Online communities are full of developers who are full of best practices and receptive to requests for help.
Can’t wait two or more weeks for a developer to get to your JavaScript task or help you track the results of your most recent survey? With Google Tag Manager, you don’t have to.
Need help setting up GTM on your site? Tag us in.