GOOGLE INCREASES LENGTH OF TITLE TAGS: WHAT NOW?
This past week, it was widely reported that Google made changes to their search results pages. One of the changes that they made was to increase the width of the main search results column. Then, since the width of the main search results column received an additional 100 pixels, there was room for Google to increase the length of title tags. Now, more of your title tag will show in the search results. The length of Title Tags has increased in the search results. Or, another way to look at it is that more keywords will show in the search results. But before you go out and update all of your title tags, you need to consider a few things.
- The length of Title Tags in Google’s search results has increased to 70–71 characters, which is up from its previous 50–60 characters.
- Just because a keyword in your title tag doesn’t show in the search results doesn’t mean that Google isn’t considering it as a part of their algorithmic review of your page.
- Well written title tags are still important.
- A good excuse to review your title tags on all pages.
- Google still may rewrite your title tag depending on the search query.
The length of Title Tags in Google’s search results has increased to 70–71 characters, which is up from its previous 50–60 characters.
Since Google increased the size of the search results column from 500 pixels to 600 pixels, they had more room for our title tags in the search results. I suspect that this increase is most likely due to the fact that more of us are using larger screens for our desktops. I use at least a 27 inch screen on my desk, and in my home office I use a 42 inch screen. On a laptop, even if it is a 15 inch laptop, the screen resolutions have gotten much better, so it’s logical that Google would make this change.
Just because a keyword in your title tag doesn’t show in the search results doesn’t mean that Google isn’t considering it as a part of their algorithmic review of your page.
If you have a title tag that is longer than what is being shown in the Google search results, Google still may use keywords that you put in your title tag. For example, if you have a blog post with a long title, there may be words in there that are relevant even though Google isn’t showing those words in the search result. In an ideal situation, though, shorter titles are better, you generally don’t want a long title that’s in the form of a sentence. Unfortunately, I still see people write title tags as if they’re a place to write a sentence. We need to think of Title Tags as if they’re a headline–and something that the Google user sees in the search results. That title tag should encourage someone to click on through to your website.
Well-written title tags are still important.
Don’t underestimate the power of a great title tag. As I mentioned before, the Title Tag should encourage someone to click on through to your website. Don’t just stuff keywords into the Title Tag because you think they will help your site rank better. Just yesterday I reviewed Title Tags on a website and the site owner had stuffed their main website’s keyword (the one keyword they want to rank for) into all Title Tags on every single page. That’s excessive and is just plain outright search engine spam.
A good excuse to review your title tags on all pages.
Google’s update of the length of Title Tags is a good time to review all of the title tags on your website. I would use something like Screaming Frog’s SEO Spider to crawl your site and review your Title Tags.
Other alternatives: review the HTML suggestions in Google Search Console. You can also use the site:yourdomain.com search query at Google to look at all of the pages they have indexed. Review all of the title tags as they appear in the search results. You may see some that need to be updated and ones that are just too long. But I would, though, crawl your own site and review the Title Tags, as there can be pages with duplicate Title Tags that Google is not indexing.
Google still may rewrite your title tag depending on the search query.
Keep in mind that at the end of the day, Google may still feel the need to rewrite your page’s Title Tag no matter how you write it. Their algorithm will decide when and for which search queries they will rewrite your Title Tag if they think you’ll get more clicks on your search result. I once saw Google rewrite every single Title Tag on a website–I simply saw what Google liked and what they didn’t, and rewrote all of the Title Tags on every page based on what Google was telling me it should be. That’s an extreme case, but if you notice that your Title Tags are being rewritten, you may want to rewrite it.
Sure, Google has given us more room for adding more keywords or words in our Title Tags. But that absolutely doesn’t mean that we need to rush out and rewrite our Title Tags. Quite the contrary. If you’ve optimized the website and you’ve done what you need to do to write great Title Tags, then this is just another change by Google. If you have good Title Tags, you don’t need to do anything.
OPTIMIZING CONTENT WITH HELP FROM GOOGLE SEARCH CONSOLE’S SEARCH ANALYTICS

As SEOs, we’re always looking for new and innovative ways to get content ideas, and optimize content on websites. Here is one way that you can optimize the content on your website at individual page level, and get content ideas for new content at the same time. Using Google Search Console (formerly called Google Webmaster Tools), you can use Search Analytics to look at each individual web page on your website and see how that page is being found in Google’s organic search results.
We’re always looking for ways to get content ideas and optimize content on websites. Here is how to optimize the content using Google Search Analytics.
Let’s go through the process, using a specific example web page, and see how we can optimize it better, update it, and maybe get some new content ideas.
First, log into Google Search Console. Select the website that you want to work on.

On the left side, choose Search Traffic, then Search Analytics, as shown above. You’ll be taken to the Search Analytics tool.
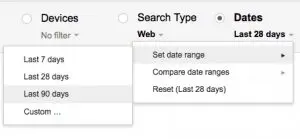
First, choose the past 90 days of time, as shown above. We’ll want to look at the maximum amount of time we can (currently 90 days) unless, of course, the page you want to analyze hasn’t been online for 90 days. But in this case, the page we’re going to analyze is a blog post that’s ranking “okay” but we want to get more organic search traffic to it. It’s been posted more than 90 days ago, so we should have plenty of data to look at.
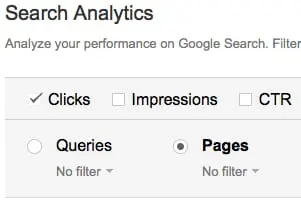
Next, choose the Pages option, as shown above.
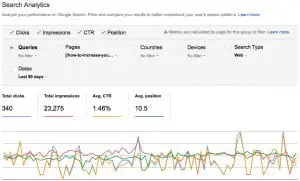
For this next step, you’ll need to click on a specific page on the list. That will take you to the individual page’s details. In the screen capture above, I went further and selected the following:
Queries
Impressions
CTR
Position
In this view (as shown in the above screen capture), we’re looking at the Search Queries for one particular page on a site, which was a blog post about increasing followers on Google Plus.
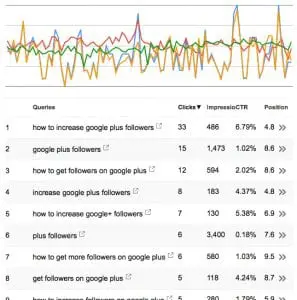
As you can see from the screen capture above, there are a lot of search queries. In this list alone there’s 200 search queries (I believe that’s the limit that Google will show). I’m showing only the first few search queries at the top of the list here.
If I were to optimize this blog post further, I would concentrate on looking at the search queries here to see how searchers are thinking about the page’s content–and what their user intent is. Based on the search queries, “how to” appears to be used a lot in search queries, so I may want to rewrite or add to the content on that page and specifically add a how-to list of action items or tasks that someone can use to increase their followers on Google Plus.
Since this page is currently ranking about #4 to #10, by getting it to rank higher for certain queries it will get more traffic. I can sort the columns by impressions to see which search queries have a lot of impressions, which is an indication of where the traffic is–so I can take advantage of it. Certainly if there is one particular keyword phrase that brings in more traffic, I’d want to adjust or rewrite the title tag and the title of the post so that it includes that keyword phrase.
Also, any social media posts promoting this content should include those keywords in the description, and any link building efforts can actually use those keywords as well. In fact, technically speaking, if I were going to build links to this page, I would use a lot of those search queries (keywords) to diversify the anchor text of links to the page–as much as I can, rather than focus specifically on one or two main keyword phrases.
By looking at the list of keywords that this page is found for, there are other search queries on the list that the content if being found for–but it’s not necessarily exactly what those searchers are looking for. Rather, here are some related keywords that are interesting, and I’d want to create more content around these keywords, perhaps linking those new blog posts to the original content (about increasing your Google Plus followers):
how to get followers on google plus business page
how to get likes on google plus
google plus management services
Finally, as you start analyzing each page of your site, you’ll find that there may be pages where the search queries that the page is being found for is totally wrong–or the user intent doesn’t appear to match the content of the page. That will allow you to figure out how to adjust the content on the page so that it reaches the right searchers.
31 REASONS WHY THE GOOGLE PENGUIN ALGORITHM HASN’T UPDATED YET
As you probably are aware, Google hasn’t updated their Google Penguin algorithm update in quite some time. In fact, it’s been so long since we have seen an update related to links that we’ve even seen small businesses literally shut their doors as a result. Certainly that’s not Google’s fault at all, but the lack of a Google Penguin update has become quite the joke and frustration for many in the search community.
Back in January 2016, Search Engine Journal reported that Google’s Next Penguin update “to happen within weeks”. Well, as of this post, it’s now been months, not weeks. Google was “aiming for launching penguin this quarter, but we don’t have a more precise timeframe”, according to Gary Illyes.

While we wait for another update, there are a few things that you can still do. We’ve detailed them here on our blog.
Here at Globe Runner, we decided that we would help Google out and list excuses why their Google Penguin algorithm hasn’t launched yet. Here are 31 reasons why the Google Penguin algorithm hasn’t been launched yet.
1. We missed the opportunity to turn it on during World Penguin Day, so we’ll have to wait another year.
2. We need to hire a few more PR (public relations) people to handle all the questions from the media that we’ll get once it launches.
3. The Quality Raters aren’t done testing it.
4. We’re still trying to figure out how to stop relying so heavily on links as a part of our algorithm. Then we won’t even need a Google Penguin update.
5. We’re waiting for Matt Cutts to come back. Wait. Did he ever leave?
6. There are browser compatibility issues that we haven’t been able to figure out yet.
7. Our lead developer is on vacation.
8. It’s all due to global warming. It’s just not cold enough for the Penguin to return.
9. There’s a bug in the code.
10. If everyone would just stop building links for just one day, we’d have enough time to catch up.
11. There’s not enough data for us to review, we need more bad links to review.
12. We haven’t received enough link spam reports, so we don’t have enough data.
13. The Quality Raters aren’t ready reviewing and rating all of the links.
14. It worked perfectly when we first ran it.
15. We’re still working on the quality of our code.
16. The junior level developers aren’t done documenting all of the changes in the code.
17. Larry asked us to add a feature that wasn’t originally in the scope.
18. There were too many developers working on it, and we had to reassign some to another project with a higher priority.
19. There are other, more high priority development projects that we are working on.
20. We’re working on the rest of the Alphabet code first.
21. There’s just not enough time in the day to get it done.
22. There’s really no such thing as a bad link. Just disavow it or nofollow it.
23. It’s taking longer than we expected for the AI to learn how to determine a bad link from a good link.
24. Rank Brain.
25. We just figured out that all along we were collecting the wrong link data. So we have to restart.
26. We were analyzing the wrong link data, but we’re all good now.
27. We forgot to commit the code that incorporates Google Penguin into the algorithm.
28. We’re waiting for y’all to stop searching, just for a few minutes, so we can turn it on.
29. Google Penguin hasn’t been integrated into the real-time algorithm yet.
30. We found a previously known bug in the code, but the project manager said not to work on it yet.
31. Gary Illyes said it isn’t ready yet.
Have any more excuses that you’d like to add to our list? Feel free to list them in the comments.
5 REASONS CLAIMED AND CORRECT ONLINE DIRECTORY LISTINGS ARE VITAL
Crucial to your online marketing strategy is the use of online directories. These directories consist of organized listings of websites, and they are managed by human beings rather than automated software. This allows you to get more control over the information available online about your business, ensuring accuracy of information and more precise implementation of online marketing strategies. This means claimed—and correct—online directory listings are not only helpful, but also absolutely vital. Here are 5 reasons why:
1. Ensures consistency: If your business has been around a little while, even if it’s just a month, there is likely a listing of it somewhere on the Internet. In many cases, these records may have inaccurate information, so claiming online directory listings allows you to correct that. This ensures the consistency of information available about your business online, thereby making you easier to find.
2. Proves ownership: Claiming your online listing provides evidence that you are the owner of your business. This allows you to promote your brand on search engines while boosting the security of your listing. When claiming your listing, you will be asked to verify your business, either by phone, mail, or email.
3. Increases online presence: Claimed listings in online directories provide links to your site, making them an excellent source for link building. This helps increase your online presence and will ultimately increase the odds that people will find their way to you when searching online for your services.
4. Increases precision: Online directories are organized by category. When you claim a listing, you will be able to place it in a category that best fits its description. This makes it far easier to find your business online as it matches relevant search criteria on search engines.
5. Boosts rankings: The categorical precision and accuracy of information provided through claiming online directory listings ultimately helps improve your odds of ranking high on search engines. Also, many search engines utilize online directories to find results that match users’ search criteria, making online directory listings absolutely vital to your overall SEO strategy.
Not only will you rank higher on search engines like Google, the consistency of information about your business will ensure that people reach you rather than find themselves awash in muddled, half-accurate data. In addition, claiming your listing will secure your right to promote your business on search engines. This ultimately gives you an edge against other businesses that have not claimed or corrected their online listings.
If you’re not sure where to start with claiming online listings, Accelerate Online Marketing is here to help you. Contact Accelerate today to get started.
HOW TO ANALYZE YOUR LINKS IN GOOGLE SEARCH CONSOLE
Recently I wrote about Negative SEO and the various forms of it. I also wrote about how to combat each form of Negative SEO. Of the several forms that I identified, many were related to links. Because the Google algorithm relies so much on links and anchor text still, it’s important to keep track of the links to your website on a regular basis. Unfortunately, Google doesn’t give you a whole lot to work with, though. Google Search Console allows you to download your links, but from there you have to figure out what to do, how to analyze them, and decide which, if any, you need to disavow. Let’s take a look at the links in Google Search Console and analyze them a bit further.
First, let’s figure out where we need to go to see the links in Google Search Console.

Once you’ve verified your site in Google Search Console (formerly called Google Webmaster Tools), navigate to the “Links to Your Site” page as shown above.
In the screen capture above, you’ll see several areas. The first area, “Who links the most” is what you’ll want to look at. Click on the “More »” link to get to the second page, as shown below:
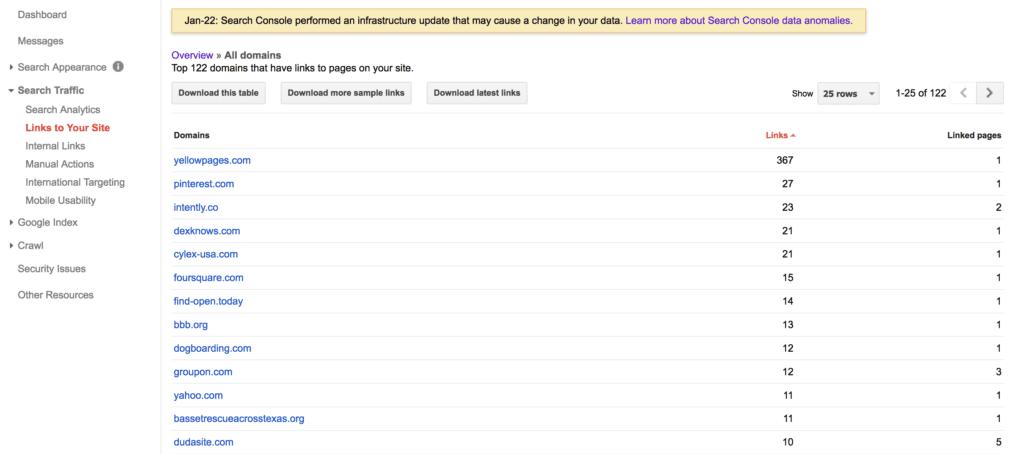
There are three separate options here to download your site’s links. The “download this table” in our case is not very helpful, so you can just ignore it. Click on the two other ones, “Download more sample links” and “Download latest links”.
Open both of these up in Microsoft Excel, which is my preferred spreadsheet application. You can certainly use Google Docs and use the Google spreadsheet app there, as well.
Once you’ve downloaded the list of links, I recommend copying and pasting one of the lists and combining that list with the other one. This way you’ll have one large list of URLs. Then, don’t forget to remove the duplicates.
At this point, you have a few options. First, you can start looking through the list of links. After sorting them alphabetically, I usually look at the URLs to see if there are any from the same website. For example, you might come across a list of 1,000 or more links from the same website. You may find that they’re a sitewide link, or the same link on a lot of web pages of one website. If you recognize the site and it’s a useful, authoritative website than fine–you may want to leave those alone. But, if they’re not useful, you may want to put them on a separate list–of links to disavow or get removed.
The next step in analyzing all of these links is to crawl the links yourself. While Google is saying that there is a link to your website, the link may no longer be valid, the site may be down, or they page may have been removed from the site that’s linking to you. So, you’ll need to crawl the list of links yourself to check them.
To crawl the links yourself, I recommend using a crawler such as the Screaming Frog SEO Spider. Screaming Frog’s SEO Spider will allow you to specify a list of links and crawl them. You should be able to learn more about each page that’s linking to you, such as the page’s title tag. If you’re savvy, you can even use the custom option to check if the link to your website still exists.

If you’d like to investigate all of these links even further, I recommend using the Majestic.com Bulk Backlinks Tool, as shown above. By uploading a list of the Google Search Console URLs, you’ll be able to focus specifically on the ones that Google is telling you about. You would want to do this for several reasons:
— If your website has a link penalty, all of the links that Google cares about will be listed here. In order to remove the penalty, you’ll need to analyze each link, get rid of the offending ones, and file a reconsideration request.
— You can look at other metrics, such as Trust Flow and Citation Flow for each link.
— You can clearly see the topics of the sites that are linking to you.
I cannot specifically tell you how to review each link and which are good links and which are bad links because every link and every link profile is different. What I can tell you, though, is that the more often you download the links to your site in Google Search Console the more often Google will refresh that data. So, download often, on a regular basis, and save the lists of links for later when you’re doing your next link analysis.
8 FORMS OF NEGATIVE SEO AND HOW TO COMBAT IT
Recently, I talked with someone who is, undoubtedly, what you could call a Black Hat SEO. We were talking about various SEO techniques, and how the techniques used have changed over the years. One comment that they made, though, was pretty interesting to me. The comment was “the new SEO is not working on your own site and making it better. It’s actually making your competitors rank worse then they are.” So, essentially, this person’s view of SEO now is not about marketing your own website and getting more links, for example. It’s doing things (legally and illegally) to hurt your competitors. In other words, it’s negative SEO.
Unfortunately, for those of us who are actively marketing our businesses, creating great content and sharing it socially, and optimizing our websites, we have to deal with negative search engine optimization. It’s here, and here to stay. There is a good chance that you’ve had to deal with it already or don’t even realize that someone is doing it to your website right now. I thought that I would outline a lot of the ways that someone can do negative SEO to your website, and how to combat each of them.
Comment Spam, Forum Spam Links
They create all sorts of links to your website, usually linking to your site with various “adult keywords”, pills, or drug names, nothing related to your website. There are literally thousands upon thousands of comments made, all using scripts or other tools to blast the comments and links to your website. The comments and links are left anywhere they can, mostly by filling out comments on abandoned blogs and abandoned forum message boards. Even those links are sometimes “nofollow” links, they still are annoying and negative.
How to Deal with Comment Spam, Forum Spam Links
There really are only a few ways to deal with these. Download the links to your site from Google Webmaster Tools on a regular basis, review the links, and disavow the domains where these links appear. Use a tool like Majestic.com or Ahrefs.com to review the anchor text of all your links. In most cases it’s easy to identify the bad anchor text, and disavow the links. You can also attempt to get those links removed, as well. I prefer to use a tool such as Rmoov.com to send out the emails to the site owners, attempting to get the links removed.
Profile Spam Links
They use profiles in order to create links to your website. The person doing negative SEO on your site will create all sorts of profiles on forums, message boards, and on social media sites and create a link back to your website. Typically these will include names of people you’ve never heard of, and don’t work for your company. The anchor text of links may include someone’s name, but it can also include adult keywords, pills or drug names or other miscellaneous words not related to your business.
How to Deal with Profile Spam Links
Typically dealing with these links requires the same technique(s) as dealing with comment spam and forum spam links, which is to identify, disavow, and remove the links. In this case, I would tend to favor the removal technique, as the site owners will, in fact, actually take the time to remove the profiles completely in many cases if you ask them.
Hacked Sites
Someone creating negative SEO links will hack into a website and make hidden text links to your website, again with “adult keyword” or pills names or drug names. They will get access to WordPress sites through various vulnerabilities, and then they’ll add the links they want. It can also include old WordPress plugins, as well. I cleaned up a client’s link profile once who had all sorts of links from hacked sites pointing to their site. I typically just contacted the site owners and told them their site was hacked. In many cases, they didn’t know their site was hacked. The hacker took time to cover their tracks, so to speak; when the site owner viewed their site they didn’t see the links because they were logged into WordPress. But when they were not logged in, the links were there. I even had to argue with site owners, telling them their site was hacked and showing them, just to get links to my client’s site removed.
How to Deal with Links from Hacked Sites
There’s not much you can do to stop someone else’s website from getting hacked. You can, though, identify the links and see that it’s happening to your site. I would immediately start notifying those sites, using a tool such as rmoov.com to send out the notices via email to those sites. It may help to file a disavow in this case, but ideally you want to get those links removed. To make sure your WordPress site isn’t hacked, I recommend using the WordFence plugin on the website.
Denial of Service Attacks or Slow Website
A denial of service attack may, in fact, be a denial of service (the attacker sends so much traffic to your website that it goes down). But, in many cases the negative SEO attacker will not want to take your site down. They will want to slow it down so much that it’s still in the search engine listings, but Google wouldn’t want to show it that much since it’s a slow site. One technique would be for the negative SEO attacker to buy ads from shady ad networks or ad networks that allow JavaScript in their ad code. Each time one of their ads is displayed, it makes a bunch of calls to your website, slowing it down. This is a distributed denial of service attack, but not in the traditional sense.
How to Deal with Denial of Service Attacks or Slow Website
First, you need to identify that this is happening to your website. I would keep up with what Google is saying in Google Analytics… look at the overall page speed. You can set up your website so that it uses a CDN (Content Delivery Network) such as CloudFlare.com, which does a good job to identify “bad traffic” so it doesn’t get to your website in the first place. The “slow website” negative SEO attack is difficult to identify, if the one doing it to your website is technically savvy so to speak. You’ll need a really advanced SEO to identify this, and it usually involves analyzing your website’s log files. If you suspect this is happening, you’ll want to make sure your site’s log files are turned on and recording every visit to your website. Then, you’ll need to hire an advanced SEO to look at the data.
Duplicate Content Negative SEO
One way that negative SEO can be done that I’ve seen involves duplicate content. Essentially, the one doing negative SEO to your site will create copies of your content and copies of your site. Then, those copies will start to appear on all sorts of other websites. Not only will they create new websites or buy expired domain names and put up the content, they’ll use other sites. I’ve seen negative SEO involve duplicate content put up on “free” or anonymous FTP sites, where they will copy your content and start FTPing it to anywhere they can. Sometimes those free FTP sites are on educational (.edu) or government (.gov) sites that will have a higher Domain Authority than your site, and can end up causing issues.
How to Deal with Duplicate Content Negative SEO
In this case, the most difficult part is identifying that it’s happening. Certainly you can search for phrases that appear on your site and see if it shows up on other sites. Sometimes you’ll just come across it randomly in the search results. There are services out there that will “watch” for duplicate copies of your site. Sites like Copyscape.com can help identify the duplicate content. To get the duplicate content taken down, you’ll need to file DMCA requests, which can be time consuming. There are sites and services that will do this in an automated fashion, but I haven’t used any of them and cannot specifically recommend any of them.
Reviews and Fake Reviews Negative SEO
Negative reviews posted about your site or your business can be annoying, but can also hurt your business. It is against the law in some jurisdictions to pay for positive reviews of your business, but I’ve seen the opposite. I’ve seen businesses pay for negative reviews of their competitors and even just post fake negative reviews.
How to Deal with Fake or Negative Reviews
Depending on where the reviews are left, you’ll need to address them. If they’re posted on Yelp or on Google, you’ll need to flag those reviews and explain why you think they should be flagged. Hopefully if it’s a pattern of negative reviews or a pattern of fake reviews they will be able to see that and remove them. So, definitely flag or report any reviews that you feel are not right. A quick response to each review, though, shows that you as a business are on top of it, and will address any complaints.
Local Negative SEO
I have seen a cases where one competitor started posting more local listings for their competitor–but the data was wrong. For example, one case had their competitor’s listings but the listing had their phone number. They started getting their competitor’s calls, which obviously benefitted them. A wrong phone number, suite number, or other garbled data on local listings can be difficult or time consuming to correct. It can, in most cases, confuse the search engines and lead to a loss of search engine rankings.
How to Deal with Local Negative SEO
The difficult part of this is to identify that it’s happening, which may in fact not be that difficult. There are services that will help you clean up your local listings and fix inaccuracies, or you can do it yourself, which is time consuming. You’ll want to identify all of the mistakes, and you can do that by simply searching for the (wrong) phone number or address and try to correct it on each site where it’s listed. Many websites simply pull in the data from another source, so you’ll need to get it corrected at the source.
Low Quality Directory Negative SEO
Several years ago the trend in SEO was to get as many links to your site as possible. Directories allowed you to get lots of links very quickly for a small fee (or for free). But, in the past few years those directories (typically copies of the DMOZ.org directory) quickly became “low quality” and not somewhere you want to be listed. Someone doing negative SEO on your website will get lots of low quality directory links to your site, usually with anchor text links not related to your website.
How to Deal with Low Quality Directory Negative SEO
Like the comment spam and forum spam links, you’ll want to identify all of these links and disavow them. I also prefer to use a service such as rmoov.com to get them removed, as well. In many cases it’s the same person who owns a lot of the same sites, and they will usually ask you to pay to get the links removed. You can pay to get them removed, but that’s totally up to you. I usually don’t pay a ransom like this.
Certainly this is not an exhaustive list of all of the ways someone can do negative SEO to your website. Those doing negative SEO are, in fact, always coming up with ways to hurt their competitors’ rankings, and it’s always evolving. As the search engines introduce more “factors” that help or hurt search engine rankings, those doing negative SEO will adapt as necessary.
Do you know of any other negative SEO techniques that I didn’t mention? Let me know in the comments so others can be aware of it.
TRULY USEFUL LINKS ABOUT LOCAL SEO IN ONE HANDY LIST
If jumping into and mastering local search engine optimization (local SEO) is your New Year’s resolution, look no further for a curated list of useful links, blogs, and other resources on the topic. We made sure to gather information that was published in the last 12 months. So bookmark this page, you’ll be referring to it frequently!
LOCAL SEO: IT’S NOT ABOUT SIZE; IT’S ABOUT GETTING FOUND.
Local SEO Tools
Every list about local SEO tools should start with the platforms that provide listing management services. These platforms partner with data aggregators to build citations — mentions of your firm on third party websites — as well as build links to your site via a plethora of directories (you may want to know those that offer follow links if this is of interest). Citations help your business rank higher for local search (see the blog section if you have a boss who needs convincing).
Perhaps the biggest benefit of using a local SEO platform is the convenience. As an entrepreneur your time is best spent building your business and selling to customers, not faffing about with manual, piecemeal submissions of your company information to directories. If you ever move, change phone numbers, rebrand, etc you will not have the nightmare of submitting 100 corrections to 100 different entities as a good platform will ensure that all changes can be centralized or, at the very minimum, reduced.
There are five local SEO platforms that are perhaps the best known in the US:
- Yext has one of the broadest service portfolios, including business pages and beacons.
- BrightLocal has over 1,600 sites in its network.
- Moz Local is an affordable investment at $84 a year if marketing budgets are very tight.
- WhiteSpark covers 42 countries which is a fantastic detail if you have a presence internationally.
- LocalEze is one of the three data aggregators supplying information to directories and search engines, and is generally credited with having the best distribution.
There are as many opinions about the best local SEO platform as there are directories to submit to — our humble opinion is, it depends on your needs, objectives and budget. Some information to check out for due diligence:
- LocalSEOChecklist displays the major players in a handy grid.
- Reddit’s SEO subreddit is worth joining, if only to lurk around discussions like this. Or this. Candid conversations and reviews by actual users: Priceless.
- SIM Partners’ white paper, Local SEO Platforms Buyer’s Guide, has a handy checklist of questions to narrow down vendor choices. (The company has its own local marketing automation platform which, to their credit, they didn’t flog in their guide.)
Local SEO Hacks and Guides
So you’re all pumped up to start. The following are pretty substantive sources that can offer a good macro view of the entire process or just one part, provide comprehensive advice to a specific sticking point, or just even serve up a local SEO topic that hasn’t been discussed before.
- Normally, pieces that advertise themselves as being ‘definitive’ fall disappointingly short, but The Site Edge’s Brian Niebler stays true to his word with Local SEO: The Definitive Guide 2016. It is a beast. Must-read!
- To demonstrate how their enterprise platform helps track rankings, SERPs also wrote a pretty meaty local SEO guide.
- Want to go totally DIY? Phil Rozek’s excellent site, Local Visibility System, has a list of local search citations that he’s collected over the past four years. He has lists for the US, UK, Canada and Australia.
- Another one for the DIYer: N.A.P. Hunter is a Chrome extension that sniffs out citations for deduplication and cleaning.
Keyword research is essential in order to create a solid foundation for your local SEO efforts. Again, there are a thousand and one opinions on the usefulness of keyword tools, but Globe Runner uses these on a daily basis:
- SEM Rush and SpyFu to find out competitors’ keywords and how they rank for these terms.
- Google Keyword Planner to determine search volumes and competition.
- Moz’s Keyword Difficulty Tool to compare/contrast their competitive figures with those of Google’s Keyword Planner — the differences can be striking and Moz has its theories on why.
- Keyword Tool to find long-tail phrases and questions people type into their browser while searching.
- Authority Labs to monitor keyword rankings for our clients and their competitors.
Local SEO Blogs to Follow
Your inbox will be nice and full everyday with these great resources on local search. And you can pick out factoids that will convince your boss that local SEO is the way to go in 2016.
- Phil Rozek’s blog on Local Visibility System is chock-a-block all about local SEO.
- The Local Search Association shares member news, statistics, industry developments and analysis pertinent to local search. Subscribe to it for excellent information such as this infographic on the top 142 categories consumers search for.
- MediaPost’s Search Marketing Daily has a roundup of the day’s SEO news from all around the web, including local SEO-focused pieces.
- Search Engine Land is always among the first to report any Google activity that could potentially impact local SEO.
- Often confused with the previously mentioned site, Search Engine Watch also has a local SEO section, albeit less frequently updated.
- Rand Fishkin’s blog on Moz is not specifically focused on the subject, but most of his marketing posts have implications for local SEO practitioners. Like this post on 2015’s keyword research tool universe or this one on Google Suggest.
Local SEO Events to Attend
You’ve read some but want to learn more about local SEO by attending conferences or meetups with fellow enthusiasts. Or you’re looking for more advanced information. Just three among the national events about local SEO to catch:
- MozCon Local 2016. The creators of Moz Local should have lots of useful information to share. February 18-19 in Seattle, WA.
- LocalU Advanced. For more experienced practitioners, here’s a conference to learn the latest on local search, mobile, analytics, web design and more. March 5 in Williamsburg, VA.
- SMX Advanced. The Local Search Advantage Workshop is a full-day dive into various advanced topics such as driving and tracking online-to-offline conversions. June 21 in Seattle, WA.
Find more national and international SEO events on this thread over at Inbound.org.
Closer to Dallas Fort Worth, Globe Runner’s home, Loco For Local will be held January 27 at La Hacienda Ranch in Grapevine. This local SEO workshop was organized for local businesses in Fort Worth, but non-FW businesses are more than welcome to drop by and exchange notes. Bill Hartzer will talk about local SEO best practices, useful tips and insider secrets.
Got any more to add? List them in the comments section.
RANKBRAIN: GOOGLE’S AI ALGORITHM
On October 26, 2015, Google unveiled its newest algorithm, RankBrain.
What is RankBrain?
RankBrain is an artificial intelligence (AI) system that sorts through Google’s indexed content and provides the most relevant websites for particular queries. RankBrain is one of many algorithms that make up Google Hummingbird. Hummingbird is Google’s overall search algorithm that consists of Panda, Penguin, RankBrain and others.
How does RankBrain work?
RankBrain is just one component of Google’s search algorithm, but its goal is to answer unique queries that Google has never seen before.
Now, according to Danny Sullivan, Google answers 100 billion searches per month. That equates to over 3 billion searches a day. On top of that, roughly 18% of daily search queries have never been asked before.
Therefore, 500+ million searches/day have never been seen before. Answering those queries has been a difficult process, but this is RankBrain’s strength.
RankBrain’s purpose is to interpret queries that may not contain the exact words/phrases that the searcher is looking for. Essentially, it attempts to re-route misguided searches.
How important is RankBrain?
According to Greg Corrado, a senior research scientist at Google, RankBrain is the third-most important ranking signal contributing to the result of a search query. That’s huge!
Google has over 200 hundred rankings signals, all of which are unknown, but highly speculated. For a Google employee to say outright that it’s the 3rd most important ranking signal is big news.
3 THINGS YOU CAN DO NOW TO OPTIMIZE YOUR IMAGES FOR MOBILE SEO
Images are like the helpful elves of content: They can aid your mobile SEO efforts by increasing engagement with users and boosting your presence on search engines. To do that however, they need to be in the best condition possible to assist you.
Here are 3 simple things you can do now to optimize images and make them fighting fit for mobile:
1. Resize your images to a size that suits mobile
It’s estimated that images make up 65% of an average page’s total size. A mobile user waiting minutes for a site to load due to 5,000 pixel pictures will navigate away to find faster alternatives. It’s critical to scale down the size of your image to allow pages to load faster.
This can be as simple as resizing images using the image preview function of your computer or using the save-for-web function in Photoshop. You can also find different tools online to resize images for social media, web pages and other purposes, or to resize/crop in bulk.
The objective is to get to as near as possible to the ideal site load speed of 1 second. Even 5 seconds can be the kiss of death for retailers.
2. Rename your files to make them more descriptive
Surprisingly a lot of people still upload photos without renaming original file names. Renaming can seem like a time waster but it actually isn’t: Many people now use Google Images to conduct a search, and we’re certain none of them involved searching for IMG688. But they are searching for the service, solution or object that your site is about.
In renaming your image files, use descriptive words and include keywords only if these are natural, not contrived.
3. Add alt text to your images
Alt text or alternative text is an attribute that allows web users to determine the contents of an image — think of it as tagging your picture with information that is helpful for viewers who can’t see it. You’ll see alt text in boxes where an image ought to be, but was stripped out.
Why add alt text? Originally alt text benefited sight impaired individuals, but now their applications have become mainstream. Like descriptive file names, alt text helps users searching for your product or service. Alt text can act as flares for your content, pointing users to your page.
You can add alt text to images and shapes very easily by right clicking and adding copy in Microsoft Office. Daunted by the prospect of adding alt text to lots of pictures? You can batch process them using tools like FastStone for PC and PhotoMill for Mac.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 12
- Next Page »